input: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|description= | |description= | ||
Allows the user to input several values at once via a modal dialog. The function takes one or more string arguments, one for each variable requiring assignment. Execution of the calling macro is paused while waiting for the user to interact with the input dialog. | Allows the user to input several values at once via a modal dialog. The function takes one or more string arguments, one for each variable requiring assignment. Execution of the calling macro is paused while waiting for the user to interact with the input dialog. | ||
Returns {{code|1}} if the user clicked the '''OK''' button, or {{code|0}} if they clicked '''Cancel''' (or hit Esc to exit the dialog). If {{code|input()}} returns 0, no variable assignments were made. | Returns {{code|1}} if the user clicked the '''OK''' button, or {{code|0}} if they clicked '''Cancel''' (or hit Esc to exit the dialog). If {{code|input()}} returns 0, no variable assignments were made. | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 19 July 2011
input() Function
Returns 1 if the user clicked the OK button, or 0 if they clicked Cancel (or hit Esc to exit the dialog). If input() returns 0, no variable assignments were made.
Usage
input(inputField, ..., ...)Parameters
inputField- A string containing various 'sub-parameters' that set the type and options of eachinputField; requires at least oneinputFieldbut will accept a reasonably large amount. TheinputFields can be set using a series of individual parameters, or as one or more String Lists. If a String List is used, the delimiter must be"##". This allows, among other things, for more dynamic input menus, with the number and type of input requests customized to the circumstances. Normally, each line is described by a string, wrapped in quotes, and the strings are separated by commas. The input function looks for unquoted commas to determine which strings are intended to be read as line entries. The function, however, can also recognize ## as a denotation of such a line break. Since this denotation can be surrounded by quotes more easily, it is possible to have a single string, wrapped in quotes, describe multiple input requests. The strings can be compiled in any number of ways: for instance using listAppend() and setting the delimiter to "##". Strings involving these ##'s can be intermixed with other standard strings. See the example below.
You declare the 'sub-parameters' of each inputField in the following manner:
"variableName|value|prompt|inputType|options"
Sub-Parameters
variableName- The name of the variable to which the value of the inputField is assigned.value- The initial value present in the dialog box. If not present, it defaults to0. In some cases you use a special syntax to indicate multiple values.prompt- The prompt displayed to the user to indicate the meaning of theinputField.inputType- Describes the type of input control presented to the user. Each of the different types are described in more detail below.options- Contains one or more options that control the appearance of the input control or how information entered in the control is treated; options are given in the formatoption=valueand separated by a space.
Input Types and Options
TEXT
Creates a text box containing the value or 0. The contents typed in the box are assigned to the variable, and there is no limit to the length of the data that can be entered.
TEXT Options
WIDTH=nnn- Sets the width of the text box; defaults toWIDTH=16.SPAN=TRUE- Causes thepromptto be hidden and allows theinputFieldto span the width of the dialog; defaults toSPAN=FALSE. If hidden theprompttext is used as a tooltip.
LIST
Creates a drop-down list of choices. The variable is assigned the index (starting at 0) of the item that was selected. The value sub-parameter is a comma delimited list of the values that can be chosen.
LIST Options
SELECT=nnn- Sets the index of the initial selection in the drop-down list (the first item is number0); defaults toSELECT=0.VALUE=STRING- The variable is assigned the string contents of the selected item instead of the index; defaults toVALUE=NUMBER.ICON=TRUE- If the string for the item contains a space and then an image asset URL, the image is displayed in the entry; defaults toICON=FALSE. Text before the URL is used for the entry's text. The getTokenImage() and getStateImage() functions can be used to obtain asset URLs.ICONSIZE=nnn- The size the icons; defaults toICONSIZE=50. All icons are stretched to fit a square this size. If the asset URL points to an image that is not square, some distortion will occur.TEXT=FALSE- No text is shown in the list entries next to the icons; defaults toTEXT=TRUE, and is ignored if no icon is set.SPAN=TRUE- Causes thepromptto be hidden and allows theinputFieldto span the width of the dialog; defaults toSPAN=FALSE. If hidden theprompttext is used as a tooltip.
CHECK
Creates a checkbox. The variable is assigned either 0 (unchecked) or 1 (checked).
CHECK Options
SPAN=TRUE- Causes thepromptto be hidden and allows theinputFieldto span the width of the dialog; defaults toSPAN=FALSE. If hidden theprompttext is used as a tooltip.
RADIO
Creates a group of radio buttons. This option works much like LIST, returning the index of the choice that was selected.
RADIO Options
ORIENT=H- Arranges the radio buttons horizontally on a single line; defaults toORIENT=V.SELECT=nnn- Sets the initially selected radio button (the first item is number0); defaults toSELECT=0.VALUE=STRING- The variable is assigned the string contents of the selected item instead of the index; defaults toVALUE=NUMBER.SPAN=TRUE- Causes thepromptto be hidden and allows theinputFieldto span the width of the dialog; defaults toSPAN=FALSE. If hidden theprompttext is used as title placed in the border of the radio button group.
LABEL
Creates a static label. The variableName is ignored, and nothing is assigned to it.
LABEL Options
ICON=TRUE- If the string for thevaluecontains a space and then an image asset URL, the image is displayed; defaults toICON=FALSE.ICONSIZE=nnn- The size the icon; defaults toICONSIZE=50. The icon is stretched to fit a square this size. If the asset URL points to an image that is not square, some distortion will occur.TEXT=FALSE- Thevalueis not shown; defaults toTEXT=TRUE.SPAN=TRUE- Causes thepromptto be hidden and allows theinputFieldto span the width of the dialog; defaults toSPAN=FALSE. If hidden theprompttext is used as a tooltip.
PROPS
Creates a bordered sub-area containing multiple text boxes, one for each entry in a String Property List stored in value. The variableName is assigned a new string property containing all the entries with their updated values.
PROPS Options
SETVARS=SUFFIXED- Makes a variable assignment for each of the sub-values, with an underscore appended to the name; defaults toSETVARS=NONE.SETVARS=UNSUFFIXED- Makes variable assignments to unmodified variable names.SUFFIXEDis usually preferred, unless you are not using variable names that match Token Properties or if you specifically intend to overwrite them.)SPAN=TRUE- Causes thepromptto be hidden and allows theinputFieldto span the width of the dialog; defaults toSPAN=FALSE. If hidden theprompttext is used as title placed in the border of thePROPSgroup.
TAB
Creates a tab for a tabbed dialog box. The variableName variable gets assigned a String Property List containing all the variable assignments made on this tab. Since some of the variables may be property strings themselves, the tab property string uses the non-default delimiter "##". When using tabs, the first inputField must be a TAB.
TAB Options
SELECT=TRUE- Causes this tab to be displayed when the dialog appears; defaults toSELECT=FALSE.
TAB Example
[H: input(
"tab0 | Info || TAB",
"Name ## Rank ## Serial number | 1,2,3 || LIST",
"tab1 | Abilities || TAB",
"Strength ## Dexterity ## Wisdom"
)]Examples
[input("AtkBonus", "DmgBonus", "CombatAdvantage")]Displays:
Note that only the variableName is required to generate an input dialog - if that is all that is provided, input() assumes that each variableName will be assigned using a text field.
2. A more complex input, including LABEL, CHECK, and TEXT fields.
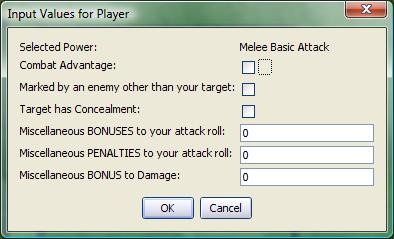
[h:status=input(
"junkVar|"+powerClicked+"|Selected Power|LABEL",
"ComAdv|0|Combat Advantage|CHECK",
"MarkPenalty|0|Marked by an enemy other than your target|CHECK",
"TargetConcealed|0|Target has Concealment|CHECK",
"MiscBonus|0|Miscellaneous BONUSES to your attack roll",
"MiscPenalty|0|Miscellaneous PENALTIES to your attack roll",
"mdb|0|Miscellaneous BONUS to Damage")]
[h:abort(status)]Displays:
Recall that junkVar, as the variableName for a LABEL control, has no value assigned to it. In this example, we assume powerClicked is a variable that is passed in some fashion to the macro generating this input. It is incorporated using the standard method of concatenating a variable into a string ("string text"+variable+"more string text"). Finally, observe that the variable status is assigned the value returned by the input() function, and the abort() function is called using the value of status. In this fashion, the macro is terminated if the user clicks the Cancel button or hits the ESC key.
3. An input showing several LIST boxes, as well as the VALUE=STRING option.
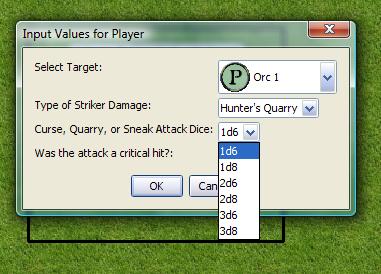
[h:status=input(
"targetNum|"+imgList+"|Select Target|LIST|SELECT=0 ICON=TRUE ICONSIZE=30",
"feature|Hunter's Quarry, Sneak Attack, Warlock's Curse|Type of Striker Damage|LIST|SELECT=0 VALUE=STRING",
"CQSDice|1d6,1d8,2d6,2d8,3d6,3d8|Curse, Quarry, or Sneak Attack Dice|LIST|SELECT=0 VALUE=STRING",
"critAttack|0|Was the attack a critical hit?|CHECK"
)]Displays:
Note that the prompt section for each list contains a list of items, or a variable containing a String List (e.g., the variable imgList). In the first list, the ICON and ICONSIZE options are set, because that list contains image asset URLs for token images. In the second two lists, the VALUE=STRING option is set so that the value in the corresponding variable is the actual string (e.g. "Sneak Attack") rather than the index of the list item.
4. An input using the "##" delimiter trick.
[h:inptext=""]
[h:num=1]
[h,foreach(entry,"SPD1,SPD2,SPD3,SPD4,SPD5,SPD6,SPD7,SPD8,SPD9"),code:{
[if(num<=CMSL),code:{
[inptext=listAppend(inptext,entry+"|"+eval(entry)+"|Level "+num,"##")]
}]
[num=num+1]
}]
[h:screen0=input(
"junkvar|Include any bonus spells from high Wisdom|Enter your Cleric spells per day|LABEL",
inptext
)]In this example, variables SPD1-SPD9 and CMSL are called earlier from a token and represent spells per day for spell levels 1-9 and the maximum spell level accessible by the token at the moment for the class in question. The macro is intended to allow manual changing of the number of spells per day for the token, but the input is cleaned up and prevents complications by not allowing for inputs to spell levels beyond what is available. The first line in the input is a standard string, followed by a comma. The second is a "##"-containing string set by the foreach() function above, which will contain just the number of input requests, separated by ##'s, needed in the situation.
5. An input using aliasmask's no-zero-trick Usually, when you leave a value blank for input it puts that annoying 0 in it's place. Here's one way to avoid that. The only limitation, I suppose is that the variable name is visible as the prompt (and the variable name/contents must be StrProp-compatible).
(thanks to aliasmask for the trick and biodude for stating the limits.)
[H: hasInput = input("Enter Table Name|tableName=||PROPS|SPAN=TRUE SETVARS=UNSUFFIXED")]6. An input using Wolph42's tooltip-trick It is possible to use HTML mark up by just adding HTML tags around the input text. This makes it possible to use e.g. bold and italic tags, but also the span tag. This span tag allows tooltips to be added anywhere via its title attribute. Here's an example:
[H: hasInput = input("someVariable|0|<html><span title='<html>This text will be shown as a tooltip if you hover with your mouse over the text</html>'>Do you wish to turn the <b>setting</b> on?</span></html>|CHECK")]input function is merely processing text and not looking at the content.