MapTool Memory Usage: Difference between revisions
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
# Type {{code|open -n "MapTool.app"}} (or whatever name your MapTool is saved as) and press '''Enter''' | # Type {{code|open -n "MapTool.app"}} (or whatever name your MapTool is saved as) and press '''Enter''' | ||
Otherwise, when you double-click an application on OS X it simply re-activates the application window that's already running. I don't know of any way of running {{code|open -n}} from the GUI although it would be a pretty simple AppleScript program ( | Otherwise, when you double-click an application on OS X it simply re-activates the application window that's already running. I don't know of any way of running {{code|open -n}} from the GUI although it would be a pretty simple AppleScript program. (It looks like it's solved here: http://superuser.com/questions/67190/how-can-i-get-an-dock-icon-to-launch-a-program-multiple-times And then this page has a description of how to do the same thing with a Ctrl-Click menu option: http://lifehacker.com/#!5766390/how-to-open-two-instances-of-an-application-in-os-x ) | ||
[[Category:MapTool]] | [[Category:MapTool]] | ||
Revision as of 17:00, 10 April 2011
How Maptool Uses Memory
When MapTool starts, the Java virtual machine (the program that lets MapTool run on your computer!) configures a number of settings for the program. Three of these settings affect the memory given to MapTool: heap memory (the memory MapTool uses to store data and resources), and stack memory (the amount of memory threads are allowed to use).
Heap memory
The heap memory allocated to MapTool indicates how much memory MapTool uses to store objects (maps, tokens, image files, macros, etc.) Heap memory allocation is controlled by two options: -Xms sets the starting heap size (the initial amount of memory MapTool is allocated) and -Xmx sets the maximum heap size (the maximum amount of memory MapTool is allowed to access).
If you set the maximum heap size too low, MapTool may run out of memory and crash, freeze, or have other problems. MapTool clients that are connecting to a server should use the same memory settings as the server when possible; otherwise clients may freeze or lose connection when using larger or more complex maps.
Stack memory
The stack memory is the amount of memory each thread is given; threads are sub-processes that handle application functions like network access, macro execution, and drawing the UI. Stack memory allocation is controlled by one option: -Xss sets the stack size (each thread is given exactly the amount specified; there is no starting or maximum stack size).
Some macro frameworks will require larger stack sizes as they perform more complex calculations and functions; they will usually specify their stack requirements. If a thread runs out of stack memory you will see a StackOverflow error and the macro will not work.
Configuring memory allocation for MapTool
In the beginning, MapTool used whatever default stack size and heap size Java felt like setting. The actual amount varied from operating system to operating system, but it was generally enough for the simple macros that were in use at the time. As the power and flexibility of the macro code increased, macros began to bump up against the limits of the default stack, and users began adjusting the stack size to compensate. As frameworks and maps became larger and more complex, users began adjusting the maximum heap size.
The amount of memory is specified in kilobytes or megabytes; "512K" is 512 kilobytes, while "512M" is 512 megabytes.
WARNING: Stack memory is allocated in addition to heap memory and each thread receives the same amount of stack memory. If you set the stack memory allocation too high, the Java VM can consume far more memory than is necessary which will affect overall computer performance.
Setting the memory allocation in a batch file
One of the ways to start MapTool is via the various script or batch files that are included when you download and unzip a copy of MapTool. There are three different types of script files included with MapTool as of 1.3.v77:
Launch MapTool.bat,Launch MapTool-512M-Memory.batandLaunch MapTool-1G-Memory.batfor Windows; the different names refer to different maximum heap allocationsLaunch MapTool.shfor Linux and Mac OS XLaunch MapTool.commandfor Mac OS X; this file can be double-clicked to start MapTool.
Editing a .bat file
Though each batch file has different heap sizes specified, the format is the same:
javaw -Xmx512M -Xss512K -jar maptool-*.jar run
To set the maximum heap size, change the -Xmx option. To set the stack size, change the -Xss option.
Editing the .sh or .command file
At the top of the shell script file are three variables:
MAXMEMSZ="768m" MINMEMSZ="32m" STACKSZ="2m"
You can set the starting heap (MINMEMSZ), maximum heap (MAXMEMSZ), and stack size (STACKSZ) by changing these variables.
Setting the memory allocation when using MapToolLauncher (Windows-only)
If you start MapTool with the Windows launcher, you can set the starting heap (Min Mem), maximum heap (Max Mem), and stack (Stack Size) sizes.
The Windows launcher defaults to a 2MB stack which is acceptable for many environments. If you change the memory values, the new values will be saved for the next launch. To reset the values, simply remove the MT.CFG file where they are saved.
Setting the memory allocation for Java WebStart (any platform)
If you start MapTool using the Java WebStart option, you can change the settings here, too.
- Go to the MapTool Launch page
- Click the CUSTOMIZATION link; three fields for setting memory options will be exposed
- You can set the starting heap (Minimum memory), maximum heap (Maximum memory), and stack size (Stack size) by changing these variables
- Click on the links above to start the application you wish to use.
If you have a saved .jnlp (Web Start) file, you can edit the memory settings by hand.
- Open the .jnlp file in a text editor
- Look for the following section (the actual memory values may differ in your copy):
<j2se version="1.5+"
initial-heap-size="64m"
max-heap-size="512m"
java-vm-args="-Xmx512m -Xms64m -Xss2m"/>
- To change the starting heap size, change the
initial-heap-sizeentry and the-Xmsentry - To change the maximum heap size, change the
max-heap-sizeentry and the-Xmxentry - To change the stack memory size, change the
-Xssentry - Save the .jnlp file
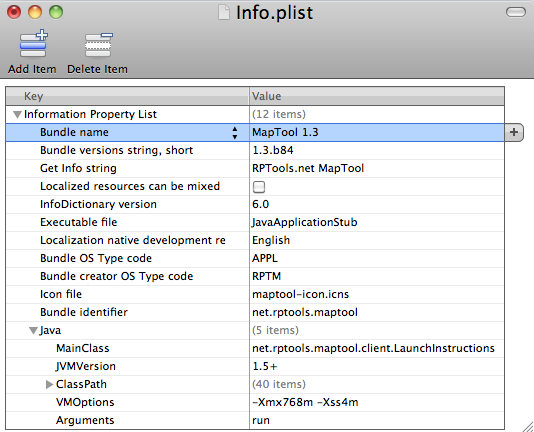
Setting the memory allocation in the Mac OS X application bundle
Users who download the .dmg (disk image) file from the RPTools download page and installed MapTool from it will see MapTool as a Mac OS X application bundle. MapTool can be launched by double-clicking it like any other Mac OS application.
- Ctrl-click (or right-click) on MapTool application icon.
- Choose Show Package Contents and a new Finder window will open.
- Open the Contents folder and locate the Info.plist file.
- Double-click that file to open the Property List Editor.
- Expand the entry for Java so it looks like the one below (it's at the bottom of the image, below).
- To set the maximum heap size, change the
-Xmxoption. To set the stack size, change the-Xssoption. To set the starting heap size, change the-Xmsoption (not depicted in the above image). - Save the file. The next time you double-click the MapTool icon, it will launch using the new memory settings.
If you want to run MapTool twice on OS X ...
You might want this for testing purposes, or perhaps you're using a dual-monitor setup where one screen shows MapTool running as a GM and the other shows MapTool running as a Player (such as a HDTV or LCD projector). In other words, you open MapTool once and start a server, then open it again and connect to the server as a client.
- Open Terminal
- Type
open -n "MapTool.app"(or whatever name your MapTool is saved as) and press Enter
Otherwise, when you double-click an application on OS X it simply re-activates the application window that's already running. I don't know of any way of running open -n from the GUI although it would be a pretty simple AppleScript program. (It looks like it's solved here: http://superuser.com/questions/67190/how-can-i-get-an-dock-icon-to-launch-a-program-multiple-times And then this page has a description of how to do the same thing with a Ctrl-Click menu option: http://lifehacker.com/#!5766390/how-to-open-two-instances-of-an-application-in-os-x )